About 12% of people experience gallstones in their lives. Gallstones occur when there are hardened bile deposits in the gallbladder, which is a pear-shaped organ on the right side of the stomach. It stores the bile and then pumps it into the small intestine.
Symptoms vary from case to case, and severity depends on the size of the stone. They can be as small as grains of sand or as large as three inches in diameter. Larger stones can settle in the bile duct and cause pain in the right side of the upper or middle abdomen, between the shoulder blades or on the right shoulder. They can also cause nausea and vomiting.
This condition is considered severe if someone is in such severe pain that they have difficulty sitting. If yellowing of the skin or white eyes, along with other symptoms appear, it means the liver is getting affected and you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
This article provided by Dr Venu Gopal Pareek gives information about the Gallstones, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment.
What Are Gallstones?
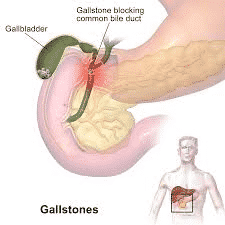
Gallstones are hard deposits of solid material that appear as stones or lumps in the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small pear-shaped organ that is on the right side of the body, just below the liver. The gallbladder stores bile, a yellowish-green liquid that supports the digestive process. Gallstones can go unnoticed until they block the bile duct and cause extreme pain and discomfort. Its size can range from large grains of sand to large golf balls and can also vary from person to person.
There are two main types of gallstones:

- Cholesterol stones: Too much cholesterol in the bile can cause the formation of green-yellow stones. They occur when the liver produces too much cholesterol compared to bile solubility capacity.
- Pigment stones: Pigments are dark brown or black and are a result of a chemical known as bilirubin. Bilirubin is naturally produced by the liver when red blood cells are damaged. However, diseases such as liver damage or blood disorders can cause an increase in bilirubin production. Stones form when the gallbladder cannot break the excess bilirubin present in the bile.
- Concentrated bile: Under normal conditions, the gallbladder empties the bile to maintain health. However, if it does not work well, bile builds up in the gallbladder and concentrates excessively, which leads to stone formation.
Symptoms of Gallstones:
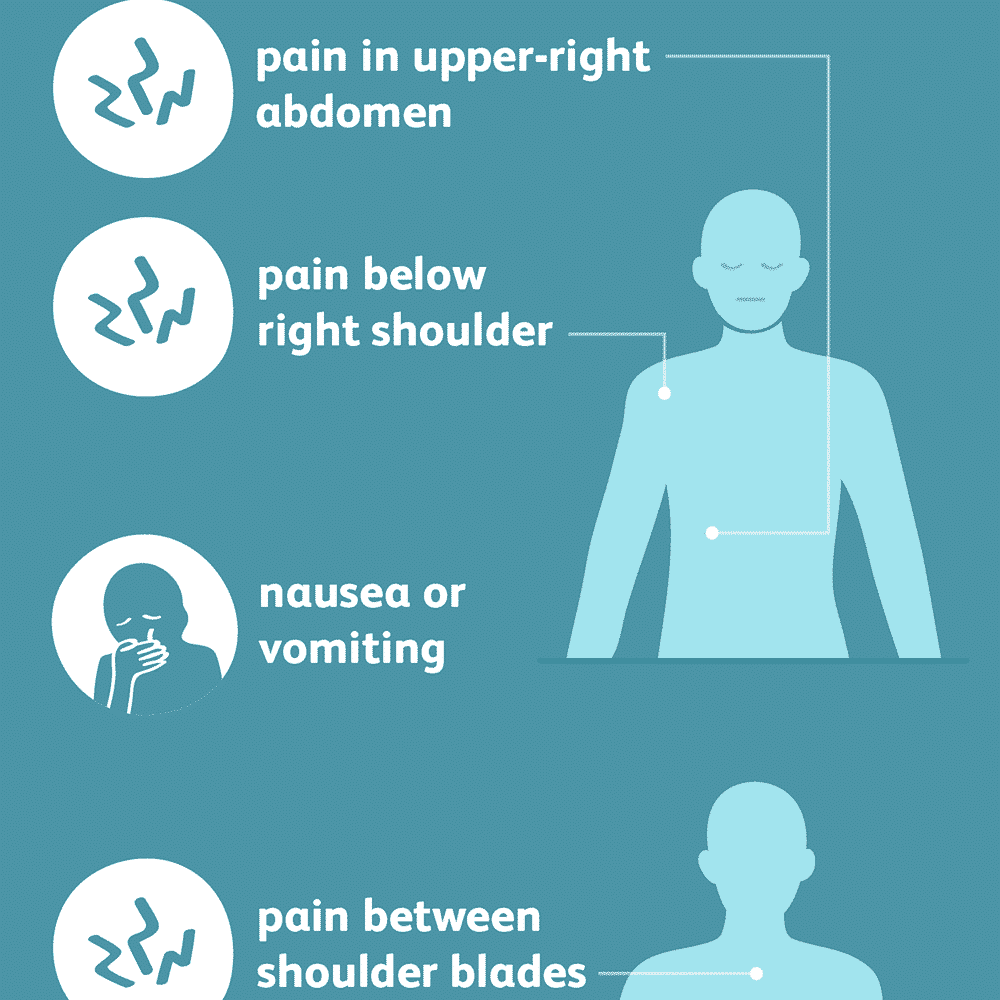
In many cases, gallstones can go unnoticed until they block the bile duct. Gallstones that show no signs need no treatment. However, it’s easy to understand the symptoms and find gallstones. Some common symptoms of gallstones are:
- Acute and rapid pain increases in the right upper abdomen
- Severe pain and rapidly increases in the middle of the stomach
- Excessive back pain, especially between the shoulders
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Foul-smelling and dark urine
- Clay-colour stool
- Excessive and uncontrollable burping
- Diarrhoea
- Indigestion
- Gallstone pain can last for several minutes or even several hours.
What Causes Gallstones?
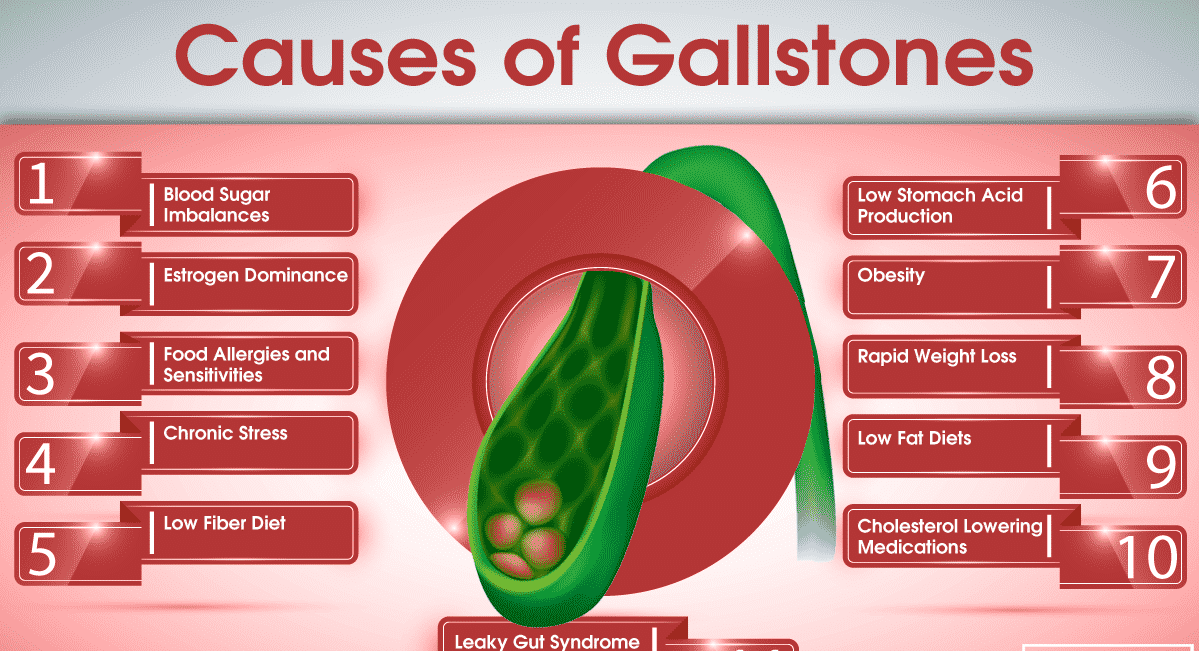
There are various reasons for the formation of these deposits in the gallbladder. The most common cause is high cholesterol levels in bile, which can clot when accumulated. Bile can usually dissolve cholesterol released from the liver. However, if the cholesterol is too high, stones are formed in the gallbladder.
Liver problems such as cirrhosis, blood disorders and bile ducts can cause gallstones. These stones have a black or brown colour and result from too much bilirubin in the gallbladder. Your body produces bilirubin because it breaks down red blood cells. Overproduction of chemicals causes gallstones.
Serious health complications can also result in inappropriate emptying of the bile ducts. In this case, bile concentrates too much on substances that crystallize and can cause stone formation. Gallstones occur when certain chemicals such as cholesterol, calcium bilirubin and calcium carbonate are disproportionate in the gallbladder. Chemical imbalance causes the formation of gallstones. Usually, the stones formed when there are:
- Excessive cholesterol
- Excessive bilirubin
- Concentrated bile
Risk Factors:
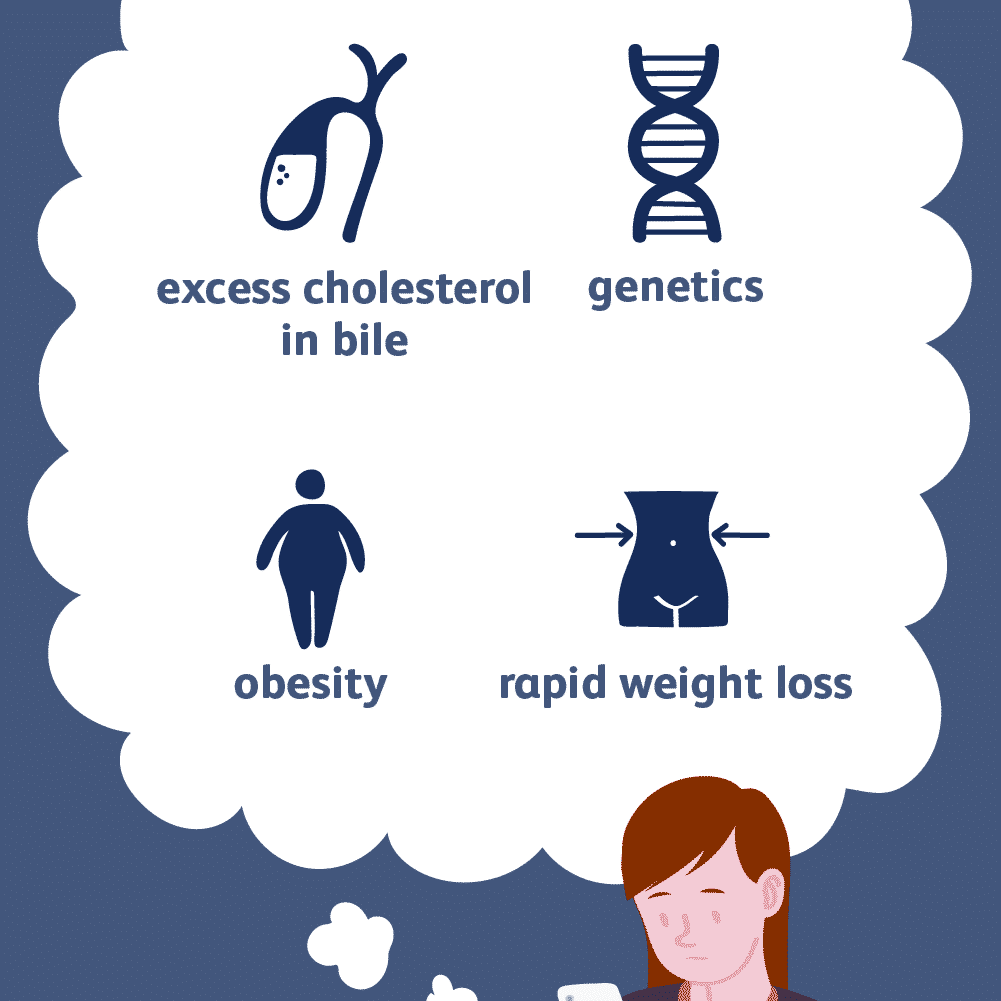
However, some risk factors are higher than others:
- Age 40 or more
- Race – Native or Mexican American
- Being female
- Obesity or overweight
- Liver disorders
- Pregnancy
- An unhealthy diet, high in fat, high in cholesterol, low in fibre, and more.
- Family history
- Diabetes
- Excessive loss of weight
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Leukaemia or other blood disorders
- Some type of medications
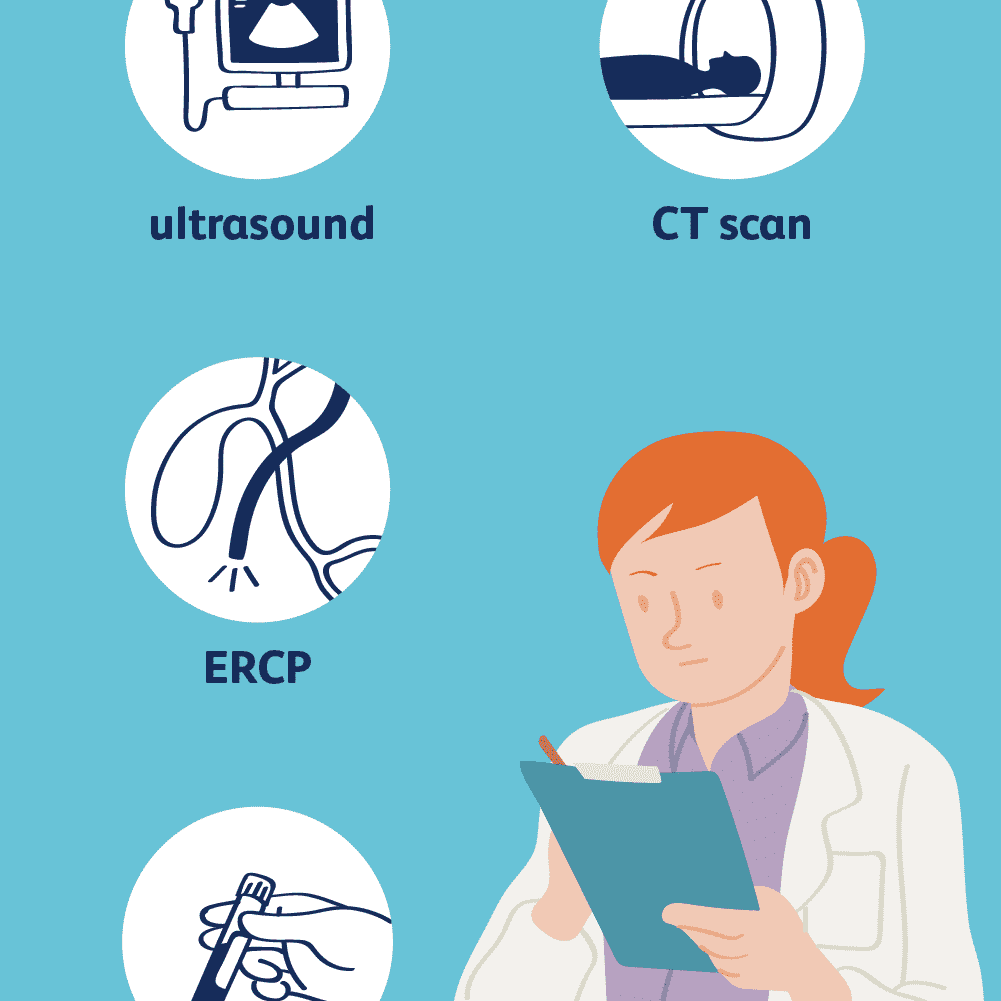
What tests used to diagnose gallstones?
If gallstones cause a problem, a liver blood test is usually done along with Ultrasound scanning of the abdomen. After the gallstones enter the bile duct, the diagnosis becomes a bit more complicated. In this case, colour x-ray dye must be injected directly into the bile duct using a needle that passes through the liver or a flexible swallowing tube.
Gallstones get treated according to their severity and frequency. If your doctor suspects that you have gallstones then blood tests, computed tomography, ultrasound scans, and tests using special dyes are done.
Treatment of Gallstones:
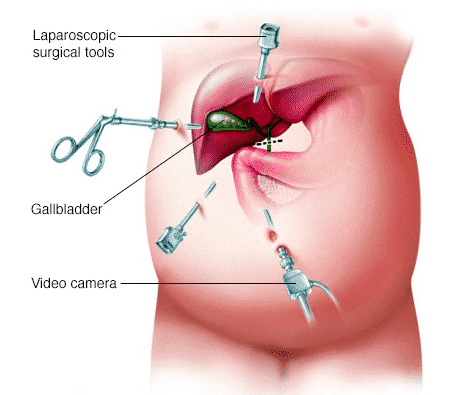
There are two ways of treatment. Your doctor may recommend drugs that can help your body to dissolve stones and relieve pain and symptoms. However, if gallstones are a health risk, removal of the gallbladder by a procedure called cholecystectomy may be recommended.
Natural treatment and home remedies: Some natural treatments such as lifestyle changes, healthy eating, and more. They can help prevent the formation of gallstones and also reduce the intensity of symptoms. Some home remedies can also work effectively to relieve pain and complications temporarily. Some tips for maintaining healthy gallbladder are:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Eat food that is enriched with nutrients
- Eat anti-inflammatory foods
- Participate in regular exercise
- Avoid foods high in fat, high in cholesterol and low in fibre
- Avoid rapid weight loss
- Take supplements that are recommended such as vitamin C, iron and lecithin
Non-surgical treatments: Non-surgical methods such as medications are considered to be less effective in treating gallstones because the procedure may take years to break, and the stones may reappear when treatment is stopped by a patient. This drug is also not preferred as the primary method because surgery is beneficial and less risky.
Surgery: The most effective and primary treatment for gallstones is laparoscopic surgery to remove the gallbladder. The patient gets anaesthesia. Then the surgeon makes 3-4 small incisions in the abdomen to place a small, thin, flexible device, like a tube to remove the gallbladder. After the gallbladder is removed, bile is diverted directly from the liver to the small intestine, which does not lead to the possibility of bile concentration or stone formation. As a result of the procedure, the loose or runny stool can occur in a person, which can be easily treated with a low-fat diet, so less bile is released. This operation is safe, fast and easy with a quick recovery period. Most patients get discharged from the hospital on the same day.
Another small form of surgery or non-invasive surgery is Lithotripsy. This uses high-energy shock waves to break large stones into smaller pieces and they are passed on their own in a few days.
Gallstone surgery can usually be done laparoscopically. Every intervention has risks, but the removal of the gallbladder will eliminate all symptoms of gallbladder disease.
Conclusion:
If you have symptoms of gallstones, contact a gastroenterologist immediately. Many people who experience gallstones have to go to the emergency room because of the severity of symptoms. Follow up meetings with specialists are essential to determine the cause of the problem and to prevent further complications.
Call today or make an appointment with Dr Venu Gopal Pareek to know more information about gallstones and for the best treatment options for severe gallstone symptoms. Contact Dr Venu Gopal Pareek at +91 91-777-77715.