The thyroid gland is a small gland that is shaped like a butterfly located in the lower front of the neck, below the voice box. The thyroid gland produces hormones that are carried through the blood to every tissue in the body. It helps regulate metabolism – the process by which the body converts food into energy. It also plays a role in maintaining the functioning of organs and helping the body retain heat.
Sometimes the thyroid produces too much hormone. Structural problems such as swelling and growth of cysts or nodules can also occur. If this problem occurs, thyroid surgery may be needed. During thyroid surgery, all or part of the thyroid gets removed. The doctor will carry out this operation in the hospital while the patient is under general anaesthesia.
At one time, thyroid disease, especially in the form of marked enlargement and excessive activity, was only treated with surgical treatment — thyroidectomy, which is a safe procedure. Over the past 50 years, there has been a lot of medical knowledge about the thyroid gland, so fewer surgical procedures are needed. However, surgical treatment is still an essential part of the treatment of many thyroid disorders.
This article Dr Venu Gopal Pareek gives the information about the thyroid gland surgery.
What Is Thyroid Gland?
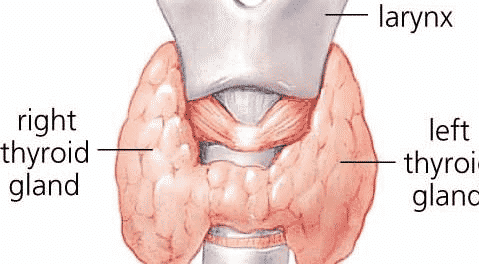
The thyroid is a 2-inch butterfly gland weighing less than one ounce located in front of the neck under larynx and consists of two lobes, one on each side of the windpipe.
The thyroid is one of the glands that form the endocrine system. The endocrine glands produce, store and secrete hormones in the blood that travels through the body and control the activities of body cells.
Thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) regulate metabolism – the way the body uses energy – and affect almost every organ in the body.
If you have a problem with the thyroid gland, then non-surgical or surgical treatment is needed. Let us know the surgical procedure in this article.
Are There Other Treatments?
Surgery is needed to get rid of lumps that get suspected of thyroid cancer. In the absence of thyroid cancer, depending on your diagnosis, there may be non-surgical treatment options. You should discuss other treatment options with your doctor who has experience with thyroid disease.
When Doctors Recommend Surgery:
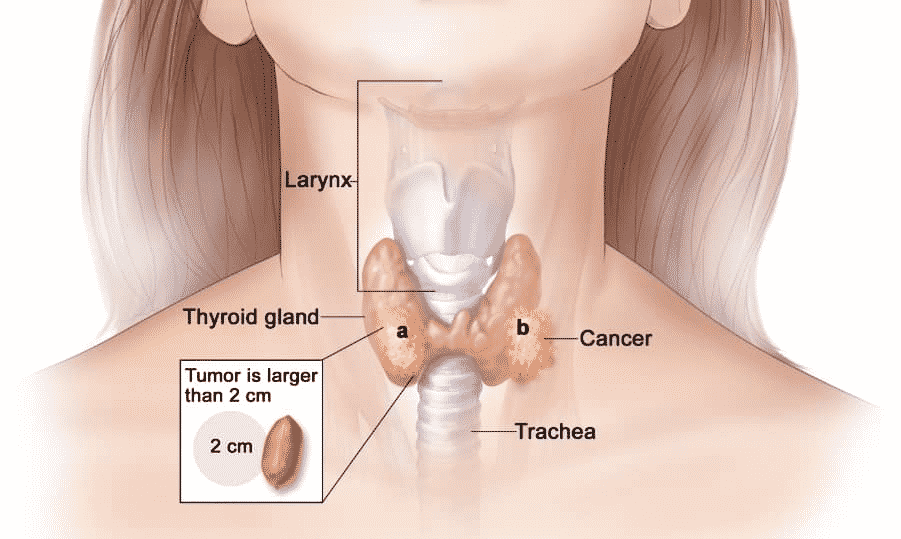
Your doctor may recommend thyroid surgery for four main reasons:
- You have a lump that might cause thyroid cancer
- Diagnosed with thyroid cancer
- You have a nodule or goitre that causes local symptoms – tracheal compression, difficulty swallowing, or a visible or ugly mass.
- You have a lump or goitre that causes symptoms due to the production and release of excess thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) – either a toxic nodule, toxic multinodular goitre, or Graves’ disease.
The extent of your thyroid surgery should be discussed with you and a thyroid surgeon and can generally classify as partial thyroid removal or full thyroid removal. The partial removal of the thyroid gland can be classified as follows: There are several types of thyroid surgery, such as:
- Biopsy or lumpectomy: Removal of a small portion of the thyroid gland.
- Lobectomy: When only half of the thyroid is removed (one lobe)
- Removal of the subtotal thyroid: If there is little thyroid tissue on both sides after surgery.
- Removal of the near-total thyroid: If only one gram of thyroid tissue remains on one side after surgery
- Complete thyroid removal: Removal of all thyroid tissue.
The recommendation for the level of thyroid surgery depends on the cause of the operation. For example, a node that grows to one side of the thyroid gland can treat with partial thyroidectomy. If you have examined for large bilateral goitre or thyroid cancer, you may have a recommendation for complete thyroid removal. However, the level of surgery is a medical decision and a personal decision and must discuss with a surgeon.
Surgery Of Thyroid Gland:
Surgery is an option for treating hyperthyroidism, but not used as often as thyroid inhibitors or radioactive iodine. Thyroid surgery is called thyroid removal and involves partial or total removal of the thyroid.
Before the procedure
Usually, the surgeon performs the removal of the thyroid by giving general anaesthesia, so you are not aware during the process. An anesthesiologist will provide you anaesthetics such as gas to inhale masks or inject liquid medicine into blood vessels. A breathing tube is then inserted into your throat to aid breathing throughout the procedure.
The surgical team then places several monitors and attaches to your body to ensure your heart rate, blood pressure, and blood oxygen remain at safe levels throughout the procedure. This monitor includes a blood pressure cuff on the arm and a heart monitor cable on the chest.
During The Procedure:
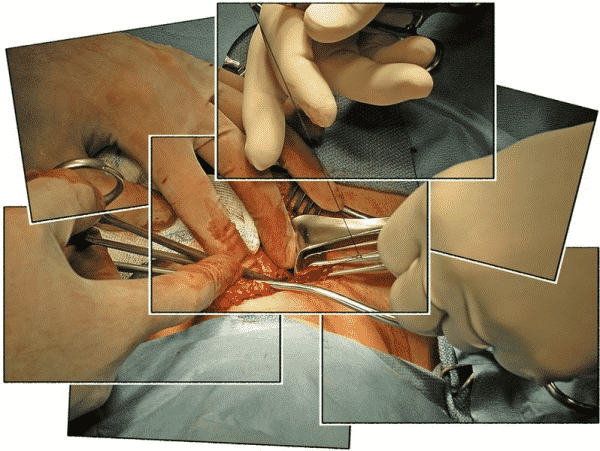
Once the patient is unconscious, the surgeon will make an incision deep in the middle of your neck. These can often insert into skin folds where it is difficult to see when the wound has healed. The thyroid gland is then wholly or partially removed depending on the cause of the surgery.
If you have thyroid removal due to thyroid cancer, the surgeon can also examine and remove the lymph nodes around the thyroid. Removal of the thyroid usually takes one to two hours. It may take more or less time, depending on the level of operation required.
There are several different approaches to removing the thyroid, including:
- Conventionally Removal Of Thyroid: This approach involves a large incision in the middle of the neck for direct access to the thyroid. Most people are likely candidates for this procedure.
- Transoral Thyroidectomy: This approach avoids wounds in the neck incision and use the incisions in the mouth.
- Endoscopic Thyroidectomy: This approach uses a small incision on the neck. Surgical instruments and small camcorders are inserted through the incision, and this camera guides your surgeon through this procedure.
Dr Venu Gopal Pareek uses the endoscopy treatment method to remove the thyroid gland, but it depends on the severity of thyroid disease in patients. The main advantages of a minimally invasive approach are that it is less pain after surgery, faster recovery, and much smaller scars than conventional methods.
Procedure Involves:
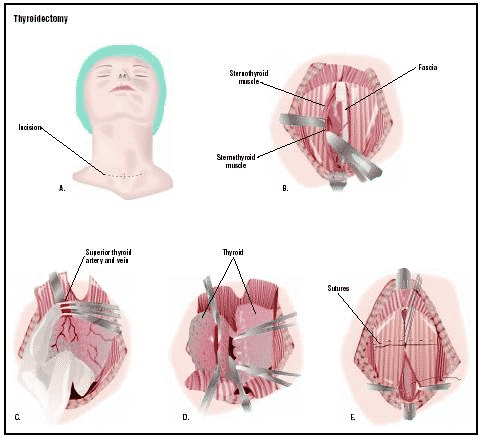
In this procedure, the surgeon cuts the base of the neck and removes most of the thyroid. With minimally invasive video-assisted thyroidectomy, the incision is made smaller, and a video camera supports the surgeon. Most operations last between 2 and 2½ hours. The patient returned home the same day or the following day after the follow-up period. While complications from thyroid surgery are rare, there are always risks with surgery.
An experienced surgeon can help prevent complications such as damage to the parathyroid gland (which causes low calcium levels) or vocal cords (which cause hoarseness invoice). After removing the thyroid gland, patients need all the time to replace their thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) with synthetic hormones.
After The Procedure:
After surgery, you will take to a recovery room where the health team will monitor your recovery after surgery. As soon as you are fully conscious, then sent to the regular room. Some people may experience drainage under an incision in the neck. This drainage is usually removed the morning after surgery.
After removal of the thyroid, many people may experience neck pain, and hoarseness or weakness in voice and these symptoms are often temporary. It does not mean that the nerves that control the vocal cords are permanently damaged. These may cause due to irritation from the breathing tube that is inserted into the respiratory tube (trachea) during surgery, or from nerve irritation caused by surgery.
After surgery, you can eat and drink as usual. Depending on the type of surgery you have performed, you may be able to return on the day of the procedure or your doctor may recommend that you stay in the hospital overnight. You are prescribed with antibiotics to avoid infection at the incision site. Take it as prescribed.
When you get home, you can usually return to your normal activities. Wait at least ten days to two weeks before doing something stronger activities such as heavy lifting or strenuous exercise.
It can take up to a year to fade the incisions scars. Your doctor may recommend the use of sunscreen to minimize scarring medications.
Some medications may include after the surgery: Thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) replacement, Calcium or vitamin D replacement.
Recovery:
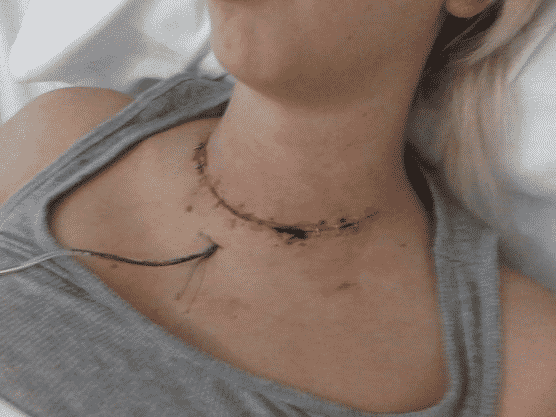
- Most people can return to normal activities the day after their thyroid surgery. Limit your physical activity or exercise for several days or weeks, or until your doctor notifies you that you are safe to start again.
- You may experience a sore throat within a few days. Over-the-counter painkillers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can usually relieve pain. If the pain is severe, the doctor can prescribe stronger pain relievers.
- After surgery, the doctor can monitor a person’s thyroid and calcium levels to determine hypothyroidism. You should tell your doctor if you experience any symptoms or hoarseness or shortness of breath.
Results After Surgery:
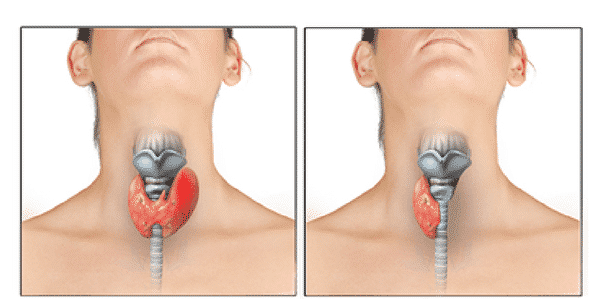
The long-term effects of thyroid removal depend on the removal of the thyroid gland.
-
- Partial Thyroidectomy:
If only part of your thyroid is removed, the rest will usually take over the function of the entire thyroid, and you may not need thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) therapy.
-
- Complete Thyroidectomy:
If all thyroid is removed, your body will not be able to make thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) , and you will develop signs and symptoms of inactive thyroid (hypothyroidism). Therefore, you need to take one tablet every day that contains synthetic thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) called levothyroxine.
This hormone replacement is identical to the hormone that is usually produced by your thyroid gland and has all the same functions. Your doctor will determine the amount of thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) replacement you need based on a blood test.
Conclusion:
Thyroid removal surgery can cure several problems. You can undergo this procedure if you have nodules or goitre in the thyroid gland, toxic nodules, Graves’ disease, or thyroid cancer. The risk of complications is low, but someone may need to take medication to replace their thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) for the rest of their lives.
Your doctor will give you detailed instructions on how to prepare for surgery and how to support a smooth recovery. Although surgery is not the most common method for treating hyperthyroidism, the right candidate for surgery is based on specific reasons for your condition and your preferences. Talk to Dr Venu Gopal Pareek at 91-777-77715 and book your appointment to know about the benefits and risks of removing the thyroid and don’t be afraid to ask. The doctor will help you and determine the best treatment option for you.