A hernia is a soft bulge that shows up under the skin. It occurs when an organ or fatty tissue of the intestine pushes through a weak spot in the belly (abdominal) muscles. Inguinal hernia(inner groin) and Umbilical hernia(belly button) are the most common type of hernias seen in children. Hernia repair in children is one of the common types of general surgical procedures performed each year.
Inguinal Hernia In Children
Inguinal Hernias are of two types:
- Direct Inguinal Hernias: Direct inguinal hernias are very rare in children. They caused due to the weakness in the abdominal wall, which allows soft tissue in the intestine to protrude through.
- Indirect Inguinal Hernias: These types of hernias are the most common type of hernias seen in children. They occur when the inguinal canal fails to close during fetal development. In such cases, the contents of the abdomen protrude through the opening.
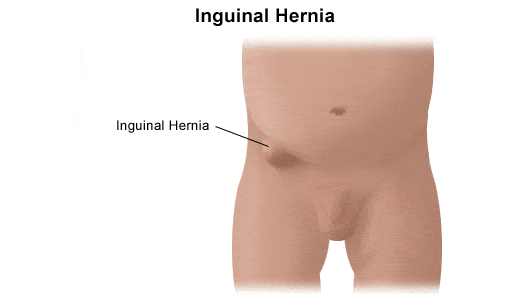
However, both boys and girls can get inguinal hernias, but boys are more likely to get inguinal hernias than girls. Even though the defect is present at the time of birth, it may or may not be visible until weeks, months, or years because of its small size. Often, inguinal hernias are detected by pediatricians during regular physical exams.
Symptoms Of An Inguinal Hernia In Children
Inguinal hernias appear like a bulge in the groin or scrotum. When the baby cries, you can see the bulge more easily and later It may go away or get smaller when the baby stops crying. Usually, when your child is calm and lying down. If you gently push the bulge, it would get smaller or might go back into the belly.
If the hernia problem becomes complicated, it shows the following symptoms:
- A small bulge between the lower abdomen and thigh, i.e., above the groin. The size increases overtime and disappears when your child is relaxing.
- Pain in the groin area, especially when your child coughing or playing and becomes normal when your child is relaxing.
- Burning sensation in the groin.
- Male children mostly have swollen scrotum.
In some cases, a child may develop a hydrocele (A fluid-filled sac around the testicle, often noticed as swelling of the scrotum) instead of a hernia, if the inguinal canal is narrow. The condition resolves on its own, else a surgery is recommended.
Treatment For Inguinal Hernia In Children
Treatment for inguinal hernias depends on your child’s symptoms, age, general health, and the severity of the condition. Most of the cases with inguinal hernias are treated surgically because the hernia might become strangulated(the intestine trapped in the inguinal canal). If this happens, the supply of blood to the intestine get stopped, and intestine possibly gets damaged.
So, a surgery called herniorrhaphy is recommended for all children suffering from inguinal hernias. During the surgical procedure, the surgeon makes a small incision in the groin and push back the contents of the hernia into
the abdomen and closes the opening with stitches. In rare conditions, a synthetic mesh might place for additional support to the weakened abdominal
lining.
The incidence of inguinal hernias is about 3-5% in infants and 13% among the infants who are born before the gestation period. One-third of childhood hernias develop in the first 6 months of life.
Umbilical Hernia In Children
An umbilical hernia is an abnormal bulge occurs at the site of the umbilicus (belly button). Usually, the umbilical ring closes before the baby is born. If the ring doesn’t close, the tissues or other organs in the intestine may protrude through the umbilical cord and forms a bulge called hernia.
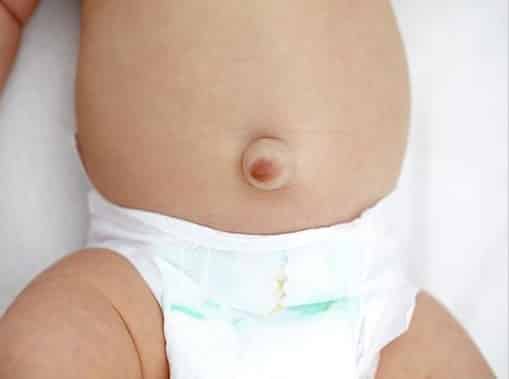
Umbilical hernias are common in newborns and children younger than 6 months. The size of umbilical hernias varies from less than 1 cm to more than 5 cm and expands when your child crying, coughing or straining during a bowel movement. The exact cause of umbilical hernias in children is yet to know, and they are most common in African Americans.
Symptoms Of An Umbilical Hernia In Children
Generally, an umbilical hernia may appear within a few weeks after birth. However, in some children, they can be noticed when they become a little older. The symptoms include:
- It occurs as a bulge or swelling in the area of belly button
- The bulge may be more evident when your child’s stomach muscles get strained during regular actions like crying, coughing, or having a bowel movement. It goes away when your baby or child relaxes or lies flat.
- In most of the children with umbilical hernia are painless.
In severe conditions like strangulation, you may notice symptoms like severe pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, and swollen belly or inability to produce a bowel movement. In such situations, consult a doctor immediately.

Treatment For Umbilical Hernia In Children
Umbilical hernias often close on their own before 1 or 2 years after birth. If the hernia is not closed by 2 to 4 years and causing problems, apparently your child needs surgery to close it.
If the condition is left untreated, the protruding tissues of a hernia can get stuck and leads to strangulation. Incarceration or strangulation is a dangerous situation where the intestine compressed hard enough to cut off the blood flow.
During the surgery, a small incision made near the belly button. If any of the intestinal parts are present in the hernia, then they are pushed back into the abdominal cavity. The opening closed by binding the skin under the navel with multiple layers of stitches to prevent another hernia. Then the cut is sealed with surgical glue which holds the edges of the wound together.
In the case of premature infants and children with specific medical conditions should be under observation in the hospital after surgery.