Around 5 million people in India develop inguinal hernias each year. Inguinal hernias, the most common type, make up 2/3 of the hernias. And roughly 90% of them are male – which might explain its reputation as a male condition. Why are only 20% of hernias repaired? Maybe because they don’t know what repair options are currently available. Repairing your hernia may be easier than you think.
Dr Venu Gopal Pareek at Sunshine Hospital performs laparoscopic hernia surgery.
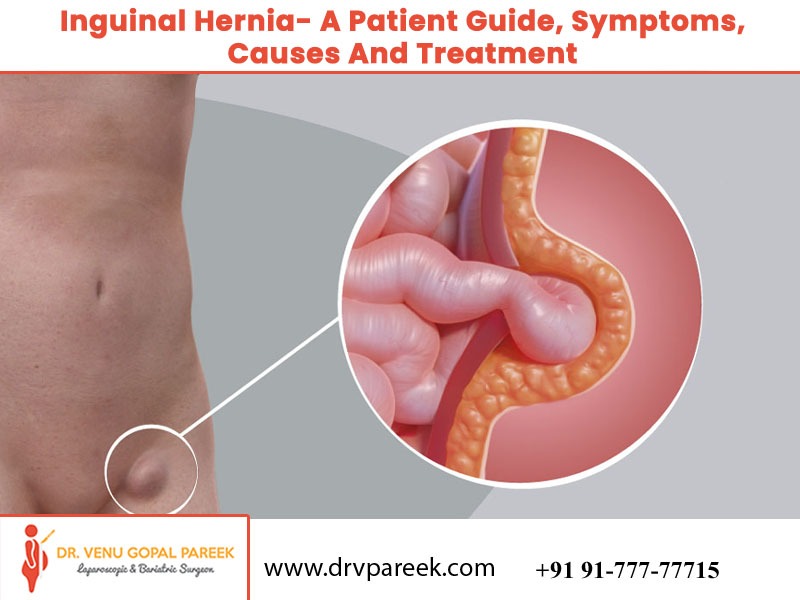
A hernia occurs when the body’s inside pushes through a weakness in the muscles or surrounding tissue walls. In most cases, the hernia causes no or exceptionally few indications, even though you’ll take note of swelling or lump within the abdomen or groin (the region between the abdomen and thighs on either side of the body).
The lumps can often be pushed back or disappear when you lie down. Coughing or straining in the abdomen area can cause lumps to appear.
This article gives information about Inguinal hernia, a patient guide, symptoms, causes and treatment, one type of hernia.
What is an inguinal hernia?
A hernia is a common condition that occurs when part of an internal organ or tissue swells through a muscle. Hernias can occur around the belly button, surgical scar, inside the diaphragm, or groin.
What is an inguinal hernia?
Inguinal hernias occur when the intestines or fat in the abdomen swell through the lower abdominal wall into the groin or groin area.
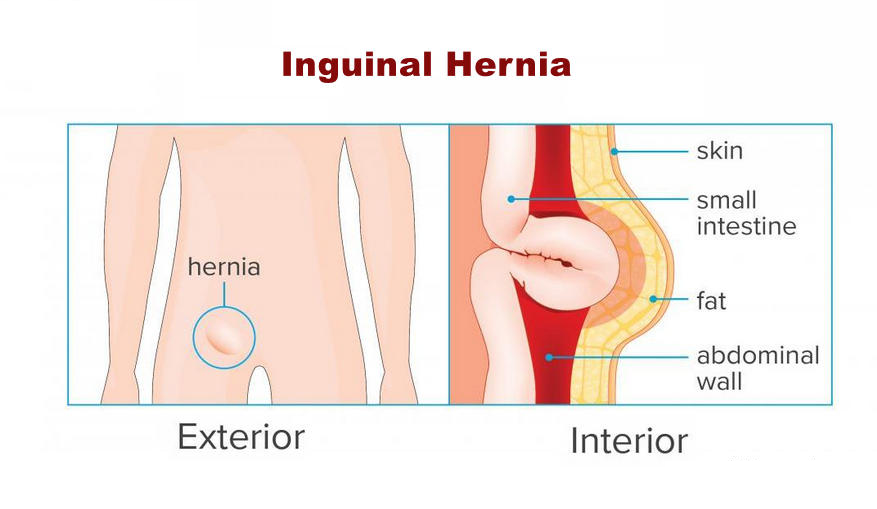
There are two types of inguinal hernias:
- Indirect inguinal hernia: This type of hernia is caused by a congenital disability in the abdominal wall that is congenital (present at birth) or acquired later.
- Direct inguinal hernia: This type of hernia usually occurs in older men. This condition is mainly caused by muscle weakness in the abdominal wall that develops over time or is caused by straining or heavy lifting.
Hernias can be on one or both sides of the groin . Direct inguinal hernias are more common later in life because the abdominal wall becomes weaker with age.
Inguinal hernias are usually harmless. However, it can be painful, especially when lifting, bending, loading a chair, or coughing. Direct hernias typically occur in older men whose abdominal muscles are weakened.
Who will get an inguinal hernia?
Men over the age of 40 are more likely than women to develop a hernia right away. About 25% of men and only about 2% of women have an inguinal hernia during their lifetime.
A family history of hernias, smoking, and men who have previously had abdominal surgery are at a higher risk of developing an inguinal hernia.
What is an incarcerated or strangulated inguinal hernia?
Inguinal hernias or shortness of breath are rare, but serious complications can occur if the hernia is not treated.
- Incarcerated hernia: This occurs when part of the abdominal fat or intestines gets stuck in the groin or scrotum and cannot return to the stomach.
- Strangulated hernia: This can occur if an incarcerated hernia is not treated. The blood supply to the intestines can be interrupted, causing the intestines to “choke”. This is a severe condition. You should see a doctor immediately if you suspect you have a closed or choking hernia.
What are the symptoms of an inguinal hernia?
Inguinal hernias can be painless or non-symptomatic, especially when they appear for the first time. Symptoms that can develop:
- A bulge on one or both sides of the groin disappears when you lie down.
- Severe pain in the groin area, especially when coughing, lifting, or exercising.
- A feeling of weakness, heaviness, or burning within the groin.
- The swollen scrotum (the sac-like part of the male genitalia under the penis).

How to diagnose an inguinal hernia?
- To diagnose an inguinal hernia, your doctor takes a detailed medical history and performs a physical exam. The person may be asked to stand up and cough so that the doctor can feel the hernia while moving in the groin or scrotum. The doctor will check if the hernia can be easily massaged back into the correct abdominal position.
- If you suspect that you or your child may have an inguinal hernia, you should see a doctor. If left untreated, an inguinal hernia can become a serious condition.
- Your doctor may ask about family history because inguinal hernias usually run in the family. He or she may then undergo a physical exam to look for a bulging hernia. You may have to cough or try to see if a hernia appears.
- An X-ray or CT scan of the abdomen may be ordered to look for an inguinal hernia and see if it is strangulated or incarcerated.
Treatment
In adults, hernias that enlarge, cause symptoms, or incarcerated are treated surgically. In the case of infants and children, the inguinal hernia is always operated on to prevent incarcerated. The surgery for an inguinal hernia is usually done on an outpatient basis. Recovery time depends on the hernia’s size, technique, and patient’s age and health. The two main types of hernia surgery are as follows:
Open hernia repair.
When repairing an open hernia, which is also known as a herniorrhaphy, a person is given a local anaesthetic to the abdomen or spine to numb the area, general anaesthesia to calm the person or help them fall asleep, or a combination of the two. The surgeon then makes an incision in the groin, moves the hernia back into the abdomen, and sutures the muscle wall. Usually, muscle weakness areas are reinforced with a synthetic mesh or filter to provide extra support – an operation called a hernioplasty.
Laparoscopic restoration of inguinal hernia
Laparoscopic surgery is performed under general anaesthesia. The surgeon makes several tiny incisions in the lower abdomen and places a laparoscope, a thin tube with a small video camera on one end. The camera gives an enlarged inside image of the body, so the surgeon can see the hernia and surrounding tissue up close on the monitor. When examining the monitor, the surgeon uses a tool to repair the hernia using a synthetic mesh carefully.
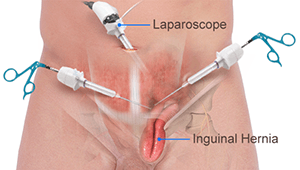
People who undergo laparoscopic surgery usually have a slightly shorter recovery time. However, the doctor may determine that laparoscopic surgery is not the best option if the hernia is massive or has had pelvic surgery.
Most adults feel uncomfortable after surgery and need pain medication. Strenuous activity and weight lifting are limited for several weeks. The doctor will discuss when a person can safely return to work. Babies and children are also unwell but usually resume normal activities after a few days.
What are the risks of inguinal hernia repair?
The risks of healing an inguinal hernia include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Pain that does not improve with treatment
Long-term complications are uncommon but can include nerve damage or a recurring hernia requiring a second surgery.
What to expect when recovering from inguinal hernia repair?
Patients who experience inguinal hernia repair are usually fine. After surgery, you may be advised to maintain a healthy weight and avoid heavy lifting or exertion during bowel movements. These steps can help prevent your inguinal hernia from returning.
- Recovery from open surgery usually requires several weeks of treatment for postoperative pain relief where minimally invasive surgery is less. You are also instructed not to lift heavy objects or do strenuous activities.
- Minimally invasive hernia surgery usually has a shorter recovery time. However, this may not be an option for those with large hernias or who previously had abdominal surgery.
- Infants and children usually recover faster than adults after hernia repair surgery.
Conclusion:
Hernia surgery is very safe and usually very effective. Depending on the hernia’s location, size, and technique, up to 10% of hernias can develop again later.
After open surgery, a person can usually resume normal activities within a week or two. With laparoscopic surgery, complete recovery usually takes a week or less. After each hernia surgery, a person should avoid heavy lifting for six to eight weeks (or as directed by a doctor) to fully heal the muscles and tissues. For more information and best surgery, contact Dr Venu Gopal Pareek at 091777 77715.