A hernia is a condition when an internal organ or tissue penetrates through holes in the muscles. Surgery to restore a hernia involves moving back the tissue that got displaced from its position, and one such procedure is Hernioplasty. In this type of surgery, a mesh patch is sutured into a weak area of tissue. Surgeons use a thin sheet of surgical mesh made either from synthetic materials.
Synthetic hernia mesh is often made from synthetic plastics called polypropylene which strengthen the torn or damaged tissue around the hernia and help it heal. This type of mesh can prevent recurrent hernias.
Some hernias are repaired using a small laparoscopic telescope as well. If your surgeon has recommended hernia repair surgery, this article can help you understand what a hernia is and what treatment options you have, and especially about inguinal hernia repair mesh.
Inguinal hernia repair:
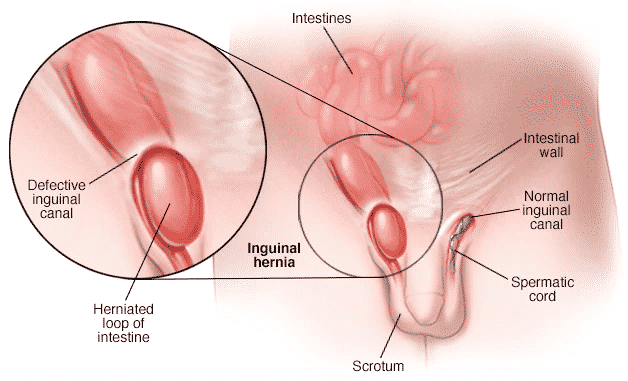
In inguinal hernias, abdominal fat or small intestine loops pass through the lower lining of the abdominal wall to a tubular inguinal canal . Hernias occur when parts of internal organs (usually the small intestine) bulge through weak points or a tear occurs in the peritoneum. This thin muscular wall holds the abdominal organs in place, resulting in a bulge. In men, hernias usually develop in the groin area near the scrotum on one or both sides (double hernias).
Types of Hernia Repair:
Different types of hernias require different types of surgery. Types of hernia surgeries include:
Herniorrhaphy (tissue repair): This is the oldest type of hernia surgery and is still in use. In this procedure, the surgeon makes a long incision just above the inguinal hernia and then opens the incision with a surgical instrument so that the surgeon has enough access for surgery. The tissue or organ removed is then returned to its original location, and the hernia sac is removed. The surgeon stitches the sides of the opening of the muscle or hole where the hernia was protruding. Once haemostasis is achieved, it is sutured.
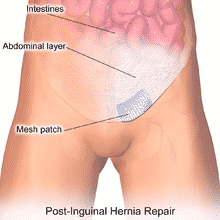
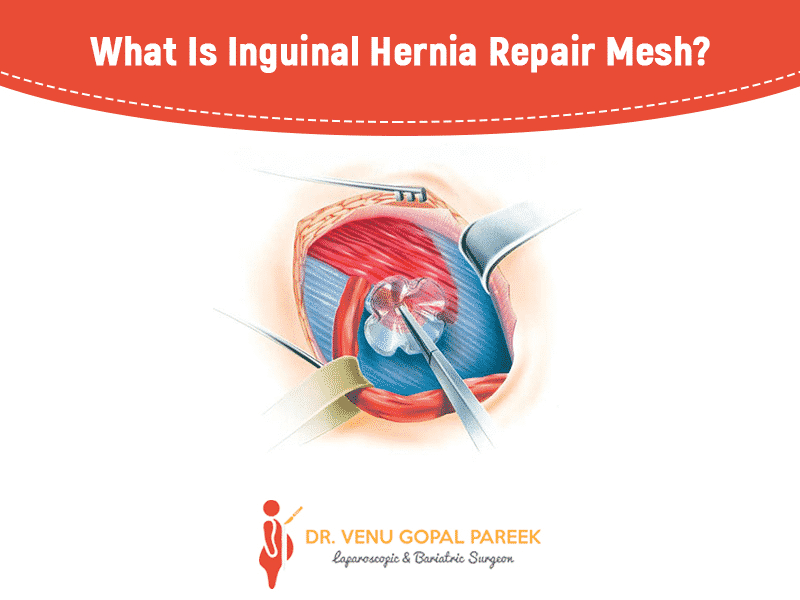
Hernioplasty (Mesh Repair): In a hernioplasty, the surgeon does not stitch the opened muscle; instead the surgeon will cover it with a flat, sterile mesh, which is usually made of flexible plastic such as polypropylene or animal tissue. The surgeon makes a small cut around the hole in the shape of the mesh and then stitches the patch into healthy, intact tissue around it. Damaged or weak tissue around the hernia uses this mesh as a supporting scaffold. Hernioplasty is better known as tension-free hernia repair. Let us see more about Hernioplasty.
Types of Surgical meshes?
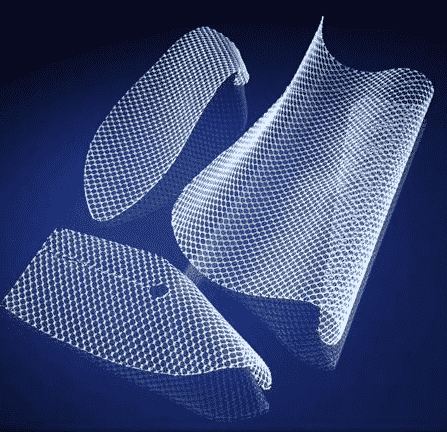
Each type of hernia mesh falls into different categories. They are classified based on their function in the body or based on the material used to make them.
Absorbable Hernia Mesh: Absorbing mesh breaks down and loses performance over time. It is not for long-term strengthening of hernias. When the material degrades, new tissue growth provides strength at the repair site.
Non-Absorbable Hernia Mesh: Non-absorbent mesh is a permanent implant. It remains in the body without any limitation. The assumption is that tissue that cannot be absorbed offers durable reinforcement at the repair site.
Synthetic Hernia Mesh: These meshes are made of synthetic materials in the form of knitted nets or non-knit sheets. Synthetic materials used can be purely non-absorbable or a combination of absorbable and non-absorbable materials. The most popular type of surgical mesh is made of polypropylene synthetic plastic.
Coated or Composite Hernia Mesh: At least one hernia repair technique can leave the mesh in touch with the intestine. It can cause the intestines to stick to the mesh. Some polypropylene meshes can be coated with digestible fatty acids, cellulose or collagen. The manufacturer claims that this coating prevents sticking.
Animal Derived Hernia Mesh: This is an absorbable mesh. Some manufacturers make hernias using animal tissue after disinfecting them. They use intestine or animal skin, usually from pigs or cows.
Why do surgeons use mesh for Herniated surgery?
The main reason why surgeons use hernia tissue is to reduce the risk of a hernia recurrence. There is a good chance that the hernia will return after repair surgery. Conventional surgical hernia sutures tear the tissue back together. Several studies have shown that mesh surgery causes fewer hernias recurrence.
Inguinal Hernia Mesh surgery:
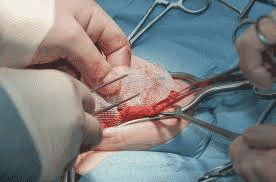
Surgery is the only treatment that can permanently repair inguinal hernias. Hernia mesh is used in about 90 per cent of these operations. Surgeons can make improvements with or without hernia mesh, but the mesh is becoming more common. Nowadays, doctors are using minimally invasive techniques called laparoscopic surgeries to implant hernias. Only small cuts are needed. The surgeon inserts the surgical instrument through an incision to implant the mesh.
Open repair is another technique that needs a large incision to open the body for hernias. The surgeon attaches the mesh to the damaged tissue and then closes the wound.
Recovery time for laparoscopic surgery is shorter, no scars are left behind, and there is less tissue damage. However, the operation takes longer and is a little expensive compared with open repair.
Surgery description:
Prominent tissue is pushed back during surgery to restore the hernia. Your abdominal wall is strengthened and supported with stitches and mesh, and this repair can be done with open surgery or laparoscopy. You and your surgeon can discuss what type of surgery is right for you. Deciding on an open procedure is the judgment of your surgeon before or during the actual operation. If the surgeon believes that it is safest to change the laparoscopic procedure into an open method, it is not a complication but good surgical judgment. The decision to switch to open procedures is based solely on patient safety.
Your surgeon will decide what type of anaesthesia you will receive in two kinds of surgeries. Let see in detail about the two surgeries.
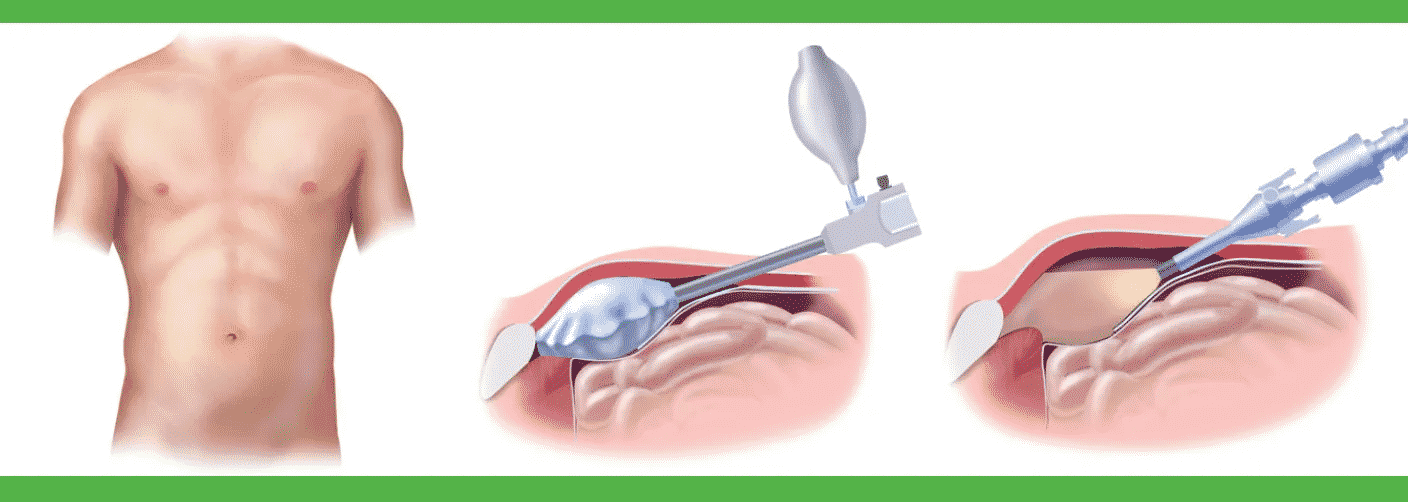
Open surgery procedure:
- The skin over hernia is cut open.
- Hernias are located and separated from the surrounding tissue. The hernia sac is removed, or the hernia is gently pushed back into the abdomen.
- The surgeon then closes the abdomen with stitches.
- Often a piece of mesh is sewn to strengthen the abdominal wall. It corrects weakness in your abdominal wall.
- The incision is sutured at the end of the repair.
Laparoscopic surgery procedure:
- The surgeon makes three to five small incisions in the lower abdomen.
- A medical device called a laparoscope is inserted through one of the incisions. The scope is a thin tube which is illuminated with a camera at the tip. It allows the surgeon to examine your stomach.
- A harmless gas CO2 is pumped into your abdomen to expand the surgery area. It provides the surgeon with more space to see and work.
- Other tools are introduced through the remaining incision. These tools are used to repair the hernia.
The same repairs are made as improvements in open surgery. - After the repair, the laparoscope and other tools are removed. The incisions are stitched and closed.
Conclusion:
Laparoscopic hernia repair is a minimally invasive procedure and thus is associated with less tissue damage and pain and recovers faster than open hernias. So, you can return home the same day and return to your previous routine activities.
If you have questions about your need for hernia surgery, alternatives, or about Dr Venu Gopal Pareek surgeon’s training and experience, please contact the surgeon at +91 91-777-77715. If you have questions about surgery or follow up, please discuss with a surgeon before or after surgery.