The gallbladder is a small pouch containing bile which is a digestive juice produced by the liver and used to break down fatty food. The gallbladder extracts water from the bile store until the liquid is very concentrated. If there are any fatty foods, then the gallbladder gets triggered to squeeze its bile concentrate into the small intestine.
Gallstones are small stones (biliary calculi) that form in the gallbladder or bile duct. They consist of cholesterol, bile pigments and calcium salts, usually in a mixture formed in the gallbladder. They are a common digestive system disorder and affect around 15 per cent of people over the age of 50. They are often not serious but unless the duct is blocked. Although gallstones do not usually cause symptoms, they can cause pain, discomfort, nausea, and vomiting.
In most cases, gallstones do not cause problems. However, prompt treatment may be needed if the stones block the channel and cause complications such as infection or inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis). Surgeons can remove your gallbladder (called cholecystectomy) if gallstones (or other types of gallbladder disease) cause problems. Techniques include laparoscopic cholecystectomy or open surgery. The gallbladder is not a vital organ, so your body can do without it quite well.
This article gives information about gallbladder stones and surgery. Dr Venu Gopal Pareek helps in the treatment of gallbladder surgery in Hyderabad. Let us see!
The structure and function of the gallbladder:
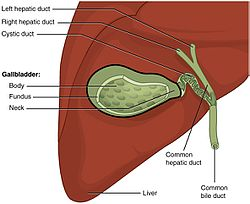
The gallbladder is a small organ like a sac in the body located under the liver in the upper right area of the abdomen. The gallbladder, along with the bile duct, pancreas and liver, is part of the body’s bile system. The bile system is responsible for the production and transportation of bile in the body.
The gallbladder stores bile juice as long as the body needs it. Bile is excreted by liver cells to help break down fat during the digestion process and to remove waste from the liver. Bile juice is in greenish-yellow colour and contains various substances such as cholesterol, bilirubin, bile salts, water, sodium and potassium. Every time someone consumes food that contains fat and cholesterol, the gallbladder squeezes and releases bile through the bile ducts, which then enter the small intestine to help the digestive process.
How gallstones are formed:
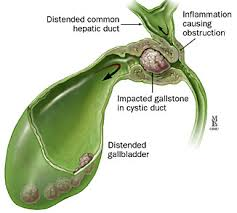
Gallstones are formed when the bile content gets imbalanced, such as excessive cholesterol, excessive bilirubin, inadequate bile salts, or when the gallbladder is not emptied regularly. Gallstones can be as small as a grain of sand and form a lump the size of a golf ball. Some stones form in the gallbladder, while others can form in the bile duct and cause obstruction.
Types of gallstones:
There are three types of gallstones:
- Mixed Stone: The most common type, consisting of cholesterol and salt. Mixed stones tend to develop in batches.
- Cholesterol stones: Mainly composed of cholesterol, fatty substances that are very important for many metabolic processes. Cholesterol stones can become large enough to block the bile duct
- Pigment stones: Have a greenish-brown colour due to certain pigments. Gallstones made of bile pigments are usually small, but many.
What Causes Gallstones:
- Fat people are more likely to have gallstones.
- Excess estrogen from multiple pregnancy, hormone replacement therapy or birth control pills can increase cholesterol levels in the bile, slow the emptying of the gallbladder and cause gallstones.
- People with bile infections can develop gallstones.
- People with congenital blood disorders such as sickle cell anaemia are more likely to develop pigment stones.
- Overeating and taking certain cholesterol-lowering drugs can also increase the risk of gallstones.
Symptoms of Gallstones:
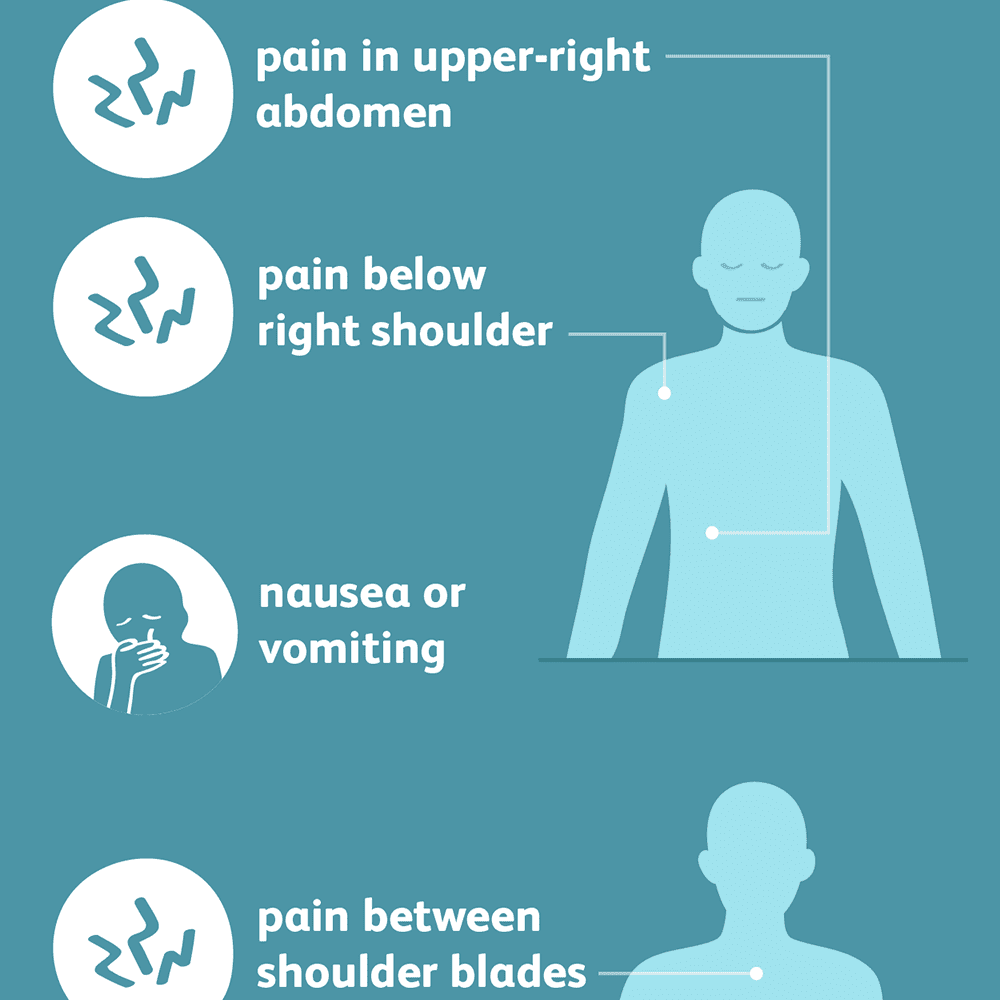
Treatment for gallstones is needed if symptoms such as severe stomach pain, often referred to as “gallstone attacks” (colic), suddenly appear. Gallstone attacks usually follow fatty foods and can occur at night. Although many patients with gallstones have no symptoms, they must be asymptomatic, and these are “silent stones”. However, a typical attack can cause:
- Severe pain in the upper right abdomen that increases rapidly and lasts from a few minutes to several hours
- Back pain between the shoulder blades
- Pain under the right shoulder
- Nausea or vomiting
Other minor symptoms of gallstones are:
- Flatulence in the stomach
- Repeated intolerance to fatty foods
- Burp
- Stomach ache
- Indesgition
Who is at risk of developing Gallstones?
- Women are more vulnerable than men
- People in their 30s and 40s
- Obese men and women
- People with rapid/sudden weight loss
- Pregnant women, women who receive hormone therapy, and women who use contraceptive pills for a long time
How to treat gallstones?
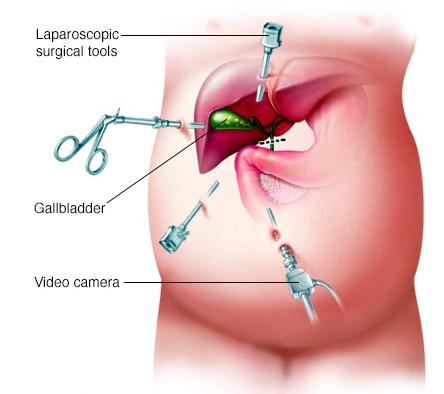
Gallstones should only be treated if they cause symptoms. For recurrent gallbladder attacks, gallbladder removal surgery or cholecystectomy is the most effective treatment. In the past, standard procedures were surgeries that required a 5-inch incision and hospitalization for up to one week. This approach has been replaced by laparoscopic cholecystectomy, in which an instrument is inserted through a small incision. This procedure only requires one night in the hospital and one week for home recovery. However, there is a low risk of injury to the bile duct, and in 5 to 10% of cases, the surgeon may need to undergo open surgery with a larger incision due to complications.
You can comfortably live without a gallbladder. The liver produces enough bile for healthy digestion. When the gallbladder separates, bile flows directly through the bile duct into the small intestine. If there is no food, the loose stool can occur. However, you can treat it with bile acid-binding drugs.
Do all gallbladder stones require surgery:

If your gallstones don’t cause symptoms, you don’t need to have surgery. You only need it if a stone comes in or blocks one of your bile ducts causing a “gallbladder attack”. Patients suffer from significant pain like a knife in the stomach that can last for several hours. For this, doctors usually recommend treatment. You can refer to a gastroenterologist, a doctor who specializes in digestive ailments or Best Gallbladder surgeon for treatment. If someone experiences a gallbladder attack, more episodes are more likely to occur.
The standard treatment for gallstones is to remove the gallbladder. If a person cannot undergo surgery, then the non-surgical treatment is to dissolve cholesterol stones in the gallbladder. Doctors can use ERCP to remove stones from a person who cannot undergo surgery or remove stones from the common bile duct in people who will undergo gallbladder surgery.
If left untreated, gallstones can also cause more severe problems, such as:
- Cholecystitis: An inflamed gallbladder
- Pancreatitis: An inflamed pancreas
- Cholangitis: An inflamed bile duct
Before deciding on surgery, a doctor will do several tests to determine what effect gallstones have on your health. Tests can include:
- Blood test
- Ultrasonic
- MRI HIDA (Hepatobiliary Iminodiacetic Acid) Scan: Radioactive chemicals injected into your body to take pictures of all blocked ducts
- Endoscopic sonography: An imaging device located in your mouth and digestive tract so that sound waves create detailed images of your small intestine.
Try other treatments before surgery:
Before considering treatment options, talk to your doctor:
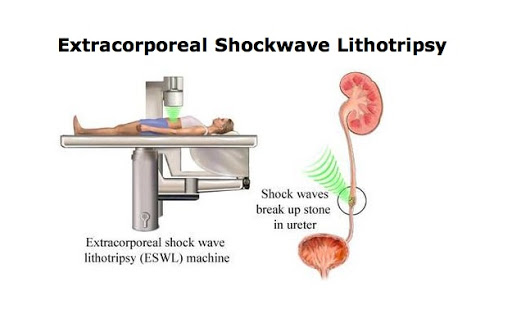
This is a very old technique tried in 1985. Results are that encouraging and patient have to receive 2-3 this treatment. It may lead to huge pain also. Gallstones tend to recur when non-surgical treatment is given, usually within five years. Non-surgical gallstone treatment includes and extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL).
Oral Dissolution Therapy:
If your gall stones in small sizes and symptoms like stomach pain and vomitings are not associated your doctor may advise taking plenty of water. Sometimes stones will be eliminated through the water itself
If the above said doesn’t work, consult the Best Gallbladder surgeons so that you can learn the pros and cons of gallbladder stone removal. Obesity is co-related to gallstone formation and that patients can make dietary changes, lose weight if they are overweight, and choose a low-fat diet. When choosing nutritional changes, consider the factors that predispose someone to gallstone: You can’t control your age, gender (women are more susceptible to gallstones), or your genes.
If you have gallstones, you can make a treatment decision if you know what is possible to be removed or treated. Discuss these treatment options with a doctor and find the right one for you.
Conclusion:
The best treatment so far is laparoscopic gallbladder surgery. Our goal is to develop a single, non-invasive treatment with minimal side effects that removes existing stones and prevents the formation of stones while at the same time exceeding cholecystectomy.
If you see anyone of the most common causes of gallbladder removal such as pain, nausea, and digestive problems, you should immediately talk to a Best Gallbladder surgeon. Don’t waste time with the pros and cons of removing the gallbladder because this operation is the only proper treatment for gallstones! For information on best gallbladder surgery or treatment contact Dr Venu Gopal Pareek at Hyderabad 091777 77715.